15 Case 2: Multiple genes
Case 2: Signature-Level Analysis of Non-B Burden Heterogeneity
Use cases: The goal of this use case is to demonstrate the application of a gene signature query for performing non-B burden analyses. As opposed to a single gene query, a multiple gene query involves comparisons not only across non-B type but also across genes. Therefore, proper normalization (gene length and non-b library size) of burdens are applied. For multiple signatures, our burden in batch module may be used to output non-B burdens for multiple gene lists.
Example: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPi) have shown efficacy in treating cancers with HR deficiencies, including those with mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, which are critical for homologous recombination (HR) repair. Non-B DNA structures are known to contribute to genetic instability and evolution, and they are recognized by DNA repair pathways, including the HR pathway. G4 stabilization can activate the HR pathway, leading to bypass/repair of G4-mediated DNA damage. Other non-B DNA structures, such as triplexes, can also interfere with HR repair, and their presence can affect genomic instability.
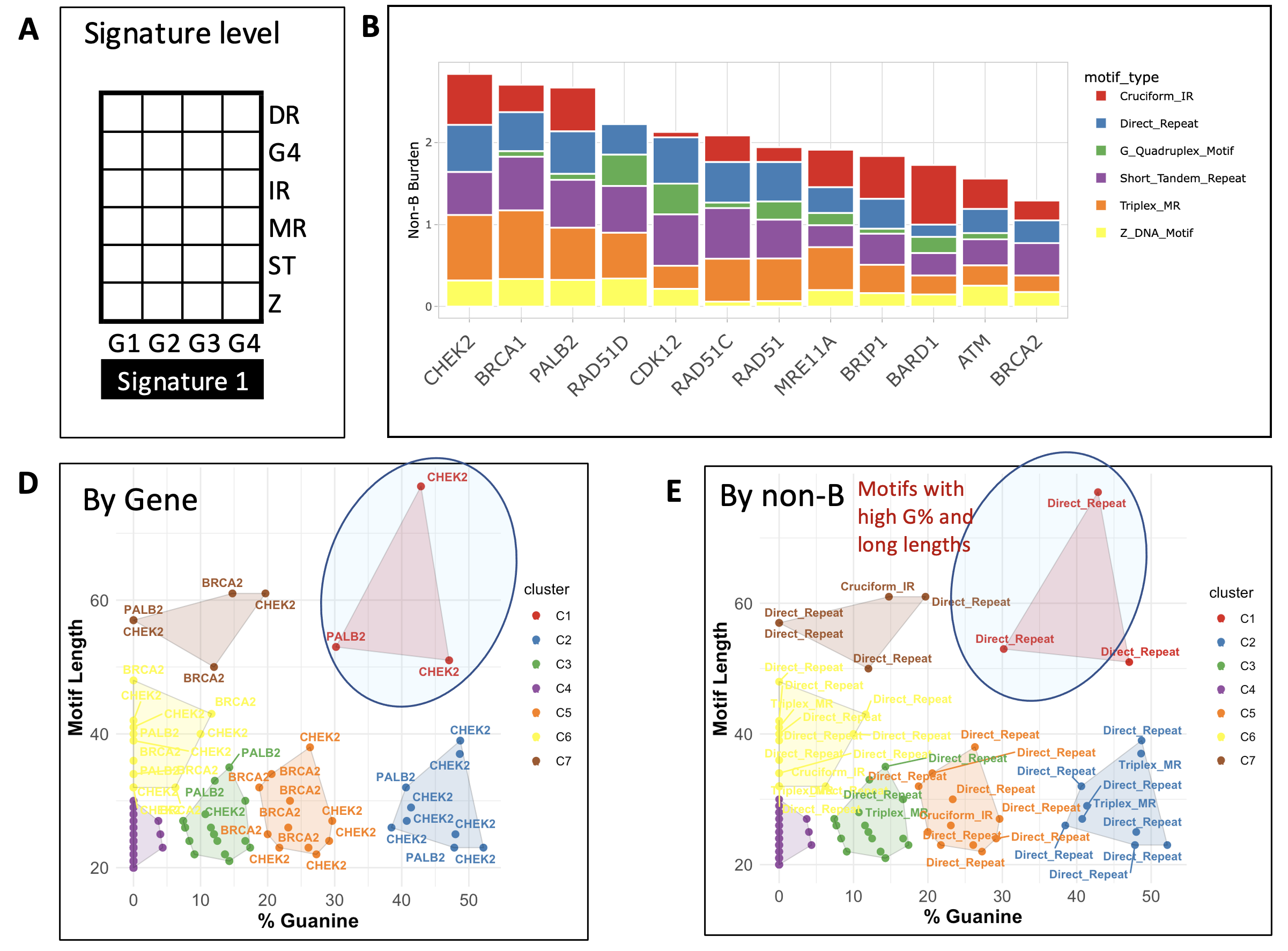
Result: We used NBBC to explore the non-B DNA forming structure heterogeneity among 12 genes in the HR pathway: BRCA1, BRCA2, MRE11A, RAD51, ATM, CDK12, PALB2, CHEK2, RAD51C, RAD51D, BRIP1, and BARD1. Using the “gene screen” interface, we derived normalized total (among non-B types) burden for each gene, which resulted in CHEK2, BRCA2, and PALB2 as the top three genes with the highest total non-B burden (A).
According to the dissection of non-B burden by each structure type, we observed that several high burdens appear to result from Triplex-forming MR, Cruciform IR and direct repeats (B). For the CHEK2 gene in particular, the main sources of non-B burdens are from Triplex-MR (burden CPKM = 0.8, Cruciform-IR (CPKM = 0.62), and direct repeat (CPKM = 0.57).
We next invoked the motif screen module and performed unsupervised clustering using motif length and %G feature. Taking CHEK2 and PALB2 for instance, there are three specific motifs associated with direct repeat forming DNA structures with relatively long length and high %G (C). Upon extracting these specific sequences, allows for their further exploration of their potential role in PARPi response.