2 Workflow
We are proud to introduce NBBC, a Non-B DNA Burden Explorer in Cancer designed for analyzing and visualizing non-B motif data. To provide an efficient and accurate means of summarizing the prevalence of non-B DNA motifs, we have developed a metric known as “Non-B Burden”. This metric allows us to analyze non-B DNA at a gene level or within a genomic region. To ensure the reliability and relevance of our data, we have sourced our non-B DNA data from the Non-B DB v2.0 database.
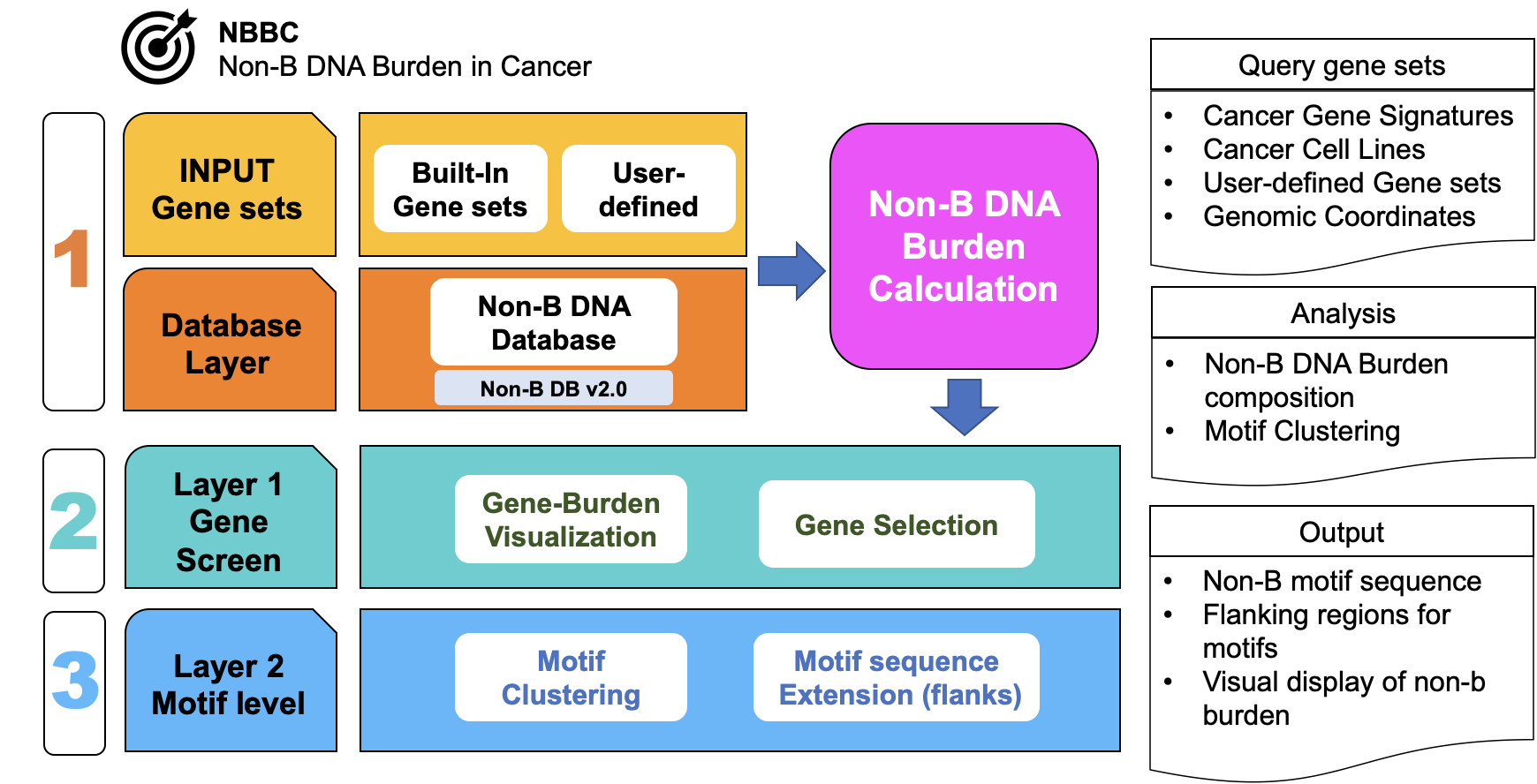
2.1 Input
NBBC has been designed to support multiple levels of gene and gene region queries to cater to a range of potential use cases. Users can input either a gene symbol (gene- or signature-level) or defined genomic regions (site-level), either individually or in batches. The app allows for single gene or region queries, queries for a group of genes or regions, and even queries for multiple groups of genes and regions.
2.2 Module1: Gene Screen
The Gene Screen analyzes non-B burden for input gene query. First, it calculates non-B burden composition for a user-input gene signature and offers multiple normalization options to enable comparisons across genes or non-B structures. It provides several visualizations for descriptive analysis of burden values, burden distribution, and burden-based gene clustering.
2.3 Module2: Motif Screen
The Motif Screen module within NBBC allows for a deeper exploration of non-B motif detection by performing sequence-level motif clustering. To determine the quality of a non-B motif, two major factors are taken into consideration - its length and guanine contents (%G). We have employed unsupervised clustering to detect non-B motifs with high G-contents and proper length. The app supports multiple features, including length, guanine, and adenine compositions in the motif sequence, for clustering.
We anticipate that NBBC will serve as a cutting-edge analysis and visualization platform for non-B DNA and genomic instability research. The app will assist users in screening genes and motifs based on non-B DNA burden, thus facilitating further understanding of the role of non-B DNA structures in cancer development and other genetic diseases.